Gum Health Matters: Preventing and Treating Gingivitis
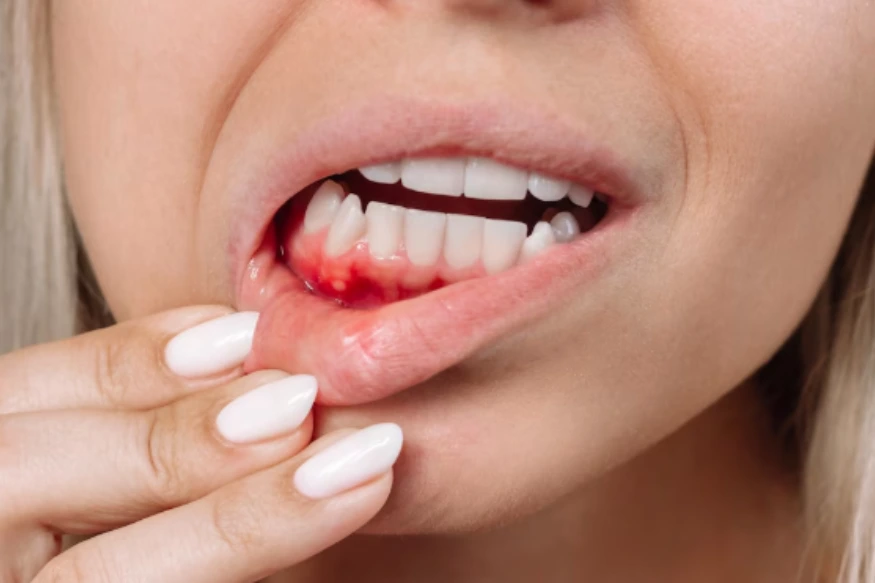
Poor oral hygiene habits don't just affect your teeth but also affect the health of the gums. Gingivitis is a common and mild form of gum disease (periodontal disease) that causes irritation, redness, and swelling (inflammation) of your gums. While this may be alarming, it can be easily managed if you catch it early.
The more you delay seeking treatment the more the gum disease will progress and weaken your gums, and surrounding bone and ultimately damage the teeth as well. Today we’ll explain what gingivitis is, how you can spot it, what causes it, and most importantly, how to treat and prevent it.
What is Gingivitis?
Gingivitis is the beginning of gum disease. It occurs when plaque, a sticky film of bacteria, builds up on your teeth. Plaque is formed when food particles mix with bacteria naturally found in your mouth. If plaque isn’t removed by brushing and flossing, the bacteria can fester and grow. This can irritate the gums, causing them to become inflamed, red, and swollen. In severe cases, gingivitis can lead to more serious gum diseases like periodontitis, which may cause tooth loss.
Although gingivitis can happen to anyone, it is completely treatable with proper care. If left untreated, however, it could develop into a more severe condition. But don’t worry – with the right knowledge and treatment, you can manage gingivitis and avoid its complications.
Causes of Gingivitis
Gingivitis is caused by the buildup of plaque on your teeth, but several factors can contribute to or increase the risk of developing it. Some of the common causes include:
- Improper Dental Hygiene: Not brushing your teeth regularly or not flossing properly allows plaque to accumulate on your teeth, leading to gingivitis.
- Bad Habits: Smoking or chewing tobacco can make you more likely to develop gum disease.
- Lack of Balanced Diet: A diet lacking essential nutrients (like vitamin C) can weaken your immune system and make it harder for your body to fight off infections, including those in your gums.
- Taking certain Medicines: Certain medications, such as steroids, phenytoin (used for treating epilepsy), and some calcium channel blockers, can cause gum enlargement or make you more prone to developing gingivitis.
- Underlying Diseases: Conditions like diabetes, certain viral or fungal infections, and hormonal changes (especially during pregnancy) can increase the risk of gingivitis.
- Increasing Age: Older adults are more likely to develop gingivitis because they may have accumulated years of plaque buildup.
- Incorrect Dental Work: Ill-fitting dental appliances or dental restorations like crowns or bridges can trap food particles and plaque, contributing to gum inflammation.
- Excessive Stress: Stress weakens your immune system, making it harder for your body to fight off infections, including gum disease.
Symptoms of Gingivitis
The symptoms of gingivitis may be mild and easy to ignore, but it’s important to notice any changes in your mouth to catch it early. Some common signs include:
- Red, swollen gums: Healthy gums should be firm and pink. In gingivitis, the gums may become red, inflamed, and swollen.
- Bleeding gums: If your gums bleed when you brush or floss your teeth, it’s a sign of gingivitis.
- Bad breath (halitosis): If you notice a persistent bad smell in your mouth, it could be a sign of gum disease.
- Tender gums: Your gums may feel sore or sensitive to the touch.
- Receding gums: In more advanced stages, gingivitis can cause your gums to pull away from your teeth.
- Loose teeth: If the condition progresses, teeth may feel loose because of gum inflammation.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s important to see a dentist. Early detection can prevent the condition from getting worse.
How to Prevent and Treat Gingivitis
The good news is that gingivitis is reversible with proper treatment and care. Let’s look at some ways you can prevent and treat gingivitis:
- Brushing and Flossing Regularly: The most effective way to prevent and treat gingivitis is by practicing good oral hygiene. This includes brushing your teeth twice a day with fluoride toothpaste. Make sure to brush for at least two minutes each time, focusing on all surfaces of your teeth and along the gumline. Flossing daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along your gumline.
- Use an Antibacterial Mouthwash: An antibacterial mouthwash can help reduce plaque and fight bacteria in your mouth. It can also help reduce inflammation and bad breath. Look for mouthwashes with active ingredients like chlorhexidine.
- Professional Dental Cleanings: Regular dental check-ups are essential for keeping your teeth and gums healthy.
- Stop Smoking or Using Tobacco Products: If you smoke or use tobacco, quitting can help reduce your risk of developing gingivitis and other serious gum diseases.
- Eat a Balanced Diet: Eating a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help support your immune system and prevent gum disease. Foods high in vitamin C, such as citrus fruits, strawberries, and bell peppers, are especially important for maintaining healthy gums.
- Manage Stress: Reducing stress through relaxation techniques, exercise, or hobbies can help strengthen your immune system and reduce your risk of gum disease.
- Use a Soft-Bristled Toothbrush: When you brush your teeth, make sure to use a soft-bristled toothbrush to prevent damaging your gums. Harder bristles can irritate or even cause your gums to recede over time.
Treatment Options for Gingivitis
If you’ve already developed gingivitis, there are several treatments your dentist may recommend:
- Teeth Cleaning: A deep cleaning procedure where the dentist removes plaque and tartar from below the gumline and smooths the tooth roots to prevent further accumulation of debris or plaque.
- Medicinal Treatment: Mouthwashes or antibiotics may be prescribed to help reduce bacteria and control infection. These treatments can be used after cleaning has been performed.
- Better Oral Hygiene: Dentist may guide you on how to improve your brushing and flossing techniques, helping you to maintain good oral hygiene and prevent gum problems in the future.
- Follow Up: After treatment, you need more frequent dental check-ups to monitor your progress and make sure your gums are healing properly.
FAQ’s
1. Is bleeding from gums normal?
No, bleeding gums are not normal. It can be a sign of gum disease or improper brushing. If it happens often, it's best to visit a dentist.
2. How can you prevent bad breath?
To prevent bad breath, brush your teeth twice a day, floss daily, and drink plenty of water. Also, clean your tongue and visit your dentist regularly.
3. Can teeth cleaning loosen teeth?
No, teeth cleaning should not loosen your teeth. If your teeth feel loose after cleaning, it might be due to other issues like gum disease, and you should see a dentist.
4. How long does teeth cleaning take?
Teeth cleaning usually takes about 30 to 60 minutes, depending on how much cleaning is needed.
